“…if you want to save your world, you must save the trees.”
J.R.R. Tolkien
If you’ve ever counted the rings on a tree stump to determine a tree’s age, you have observed how trees grow: they add a new layer of wood in each growing season. The new growth doesn’t come from the center of the tree trunk — it all happens on the outer ring. The living part of a tree trunk is just inside the protective bark.
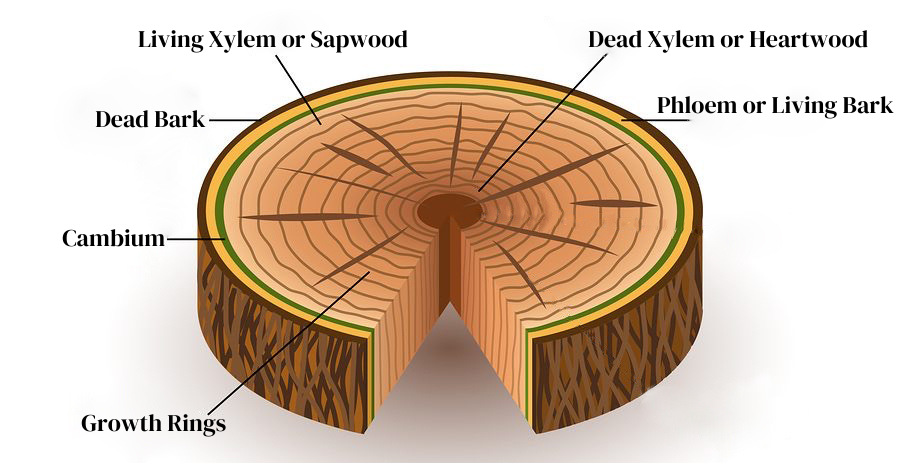
Immediately under the bark is a layer of spongy tissue called the “phloem” (pronounced “flow-um”). The phloem carries carbohydrates, manufactured by the leaves during photosynthesis, downward to the rest of the tree. The upward flow of water and nutrients from the roots happens in the “xylem” or “sapwood,” just inside the phloem. Sandwiched between these two critical vascular layers is the “cambium,” only a few microscopic cells thick, which is the actively growing part of the trunk. The cambium produces a new layer of phloem on the outer edge, and a new layer of xylem on the inside, each season.
As a tree ages, the xylem closest to the center of the tree hardens from the inner trunk outward with compounds that make the wood strong. The hard inner layer of the xylem, which is no longer alive and no longer carries water, is called “heartwood.” The older the tree, the more heartwood there is at the center, and that is the part of the tree we use for wood products.
But the living part of the tree is in those outer layers, just under the bark. Looking at the tough exterior of an old tree, it is easy to forget that the tree’s essential life process is just a few millimeters below that rugged outer surface — and it’s very vulnerable to damage.
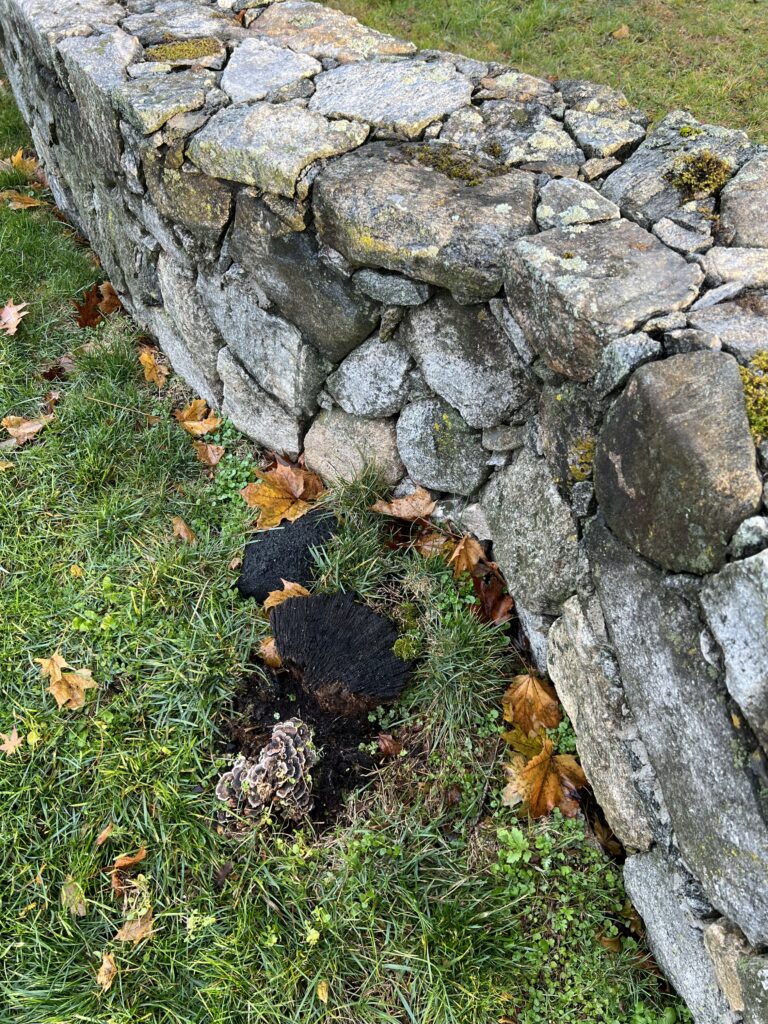
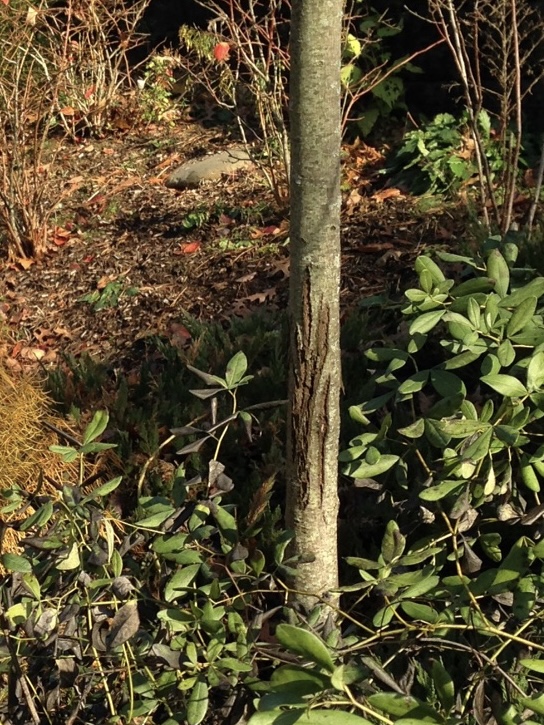
Cutting through the living tissue of a tree trunk all the way around the tree is called “girdling” and is a very effective way to kill a tree. Girdling cuts off the essential movement of nutrients up and down the tree, and severs the cambium, preventing growth. Girdling is sometimes used intentionally to kill trees before cutting them down. Unfortunately, it also sometimes happens unintentionally.
Understanding that the outer layer of a tree trunk or branch is the most vulnerable part should make us think more carefully about how we use trees and what we allow to interfere with a tree’s growth.
One common mistake is leaving tree support stakes in place too long. Unless a new tree is very top-heavy, it is usually unnecessary to stake it or use supports at planting. But if it is necessary, care should be taken to remove the supports well before the tree begins adding significant growth at the trunk.
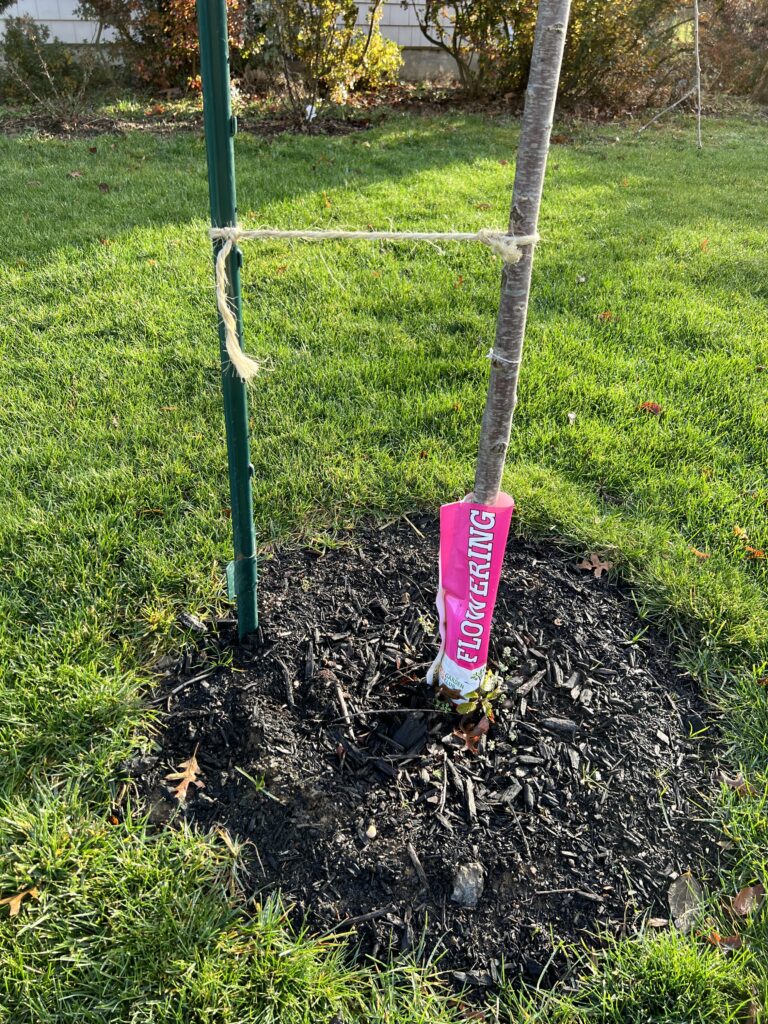
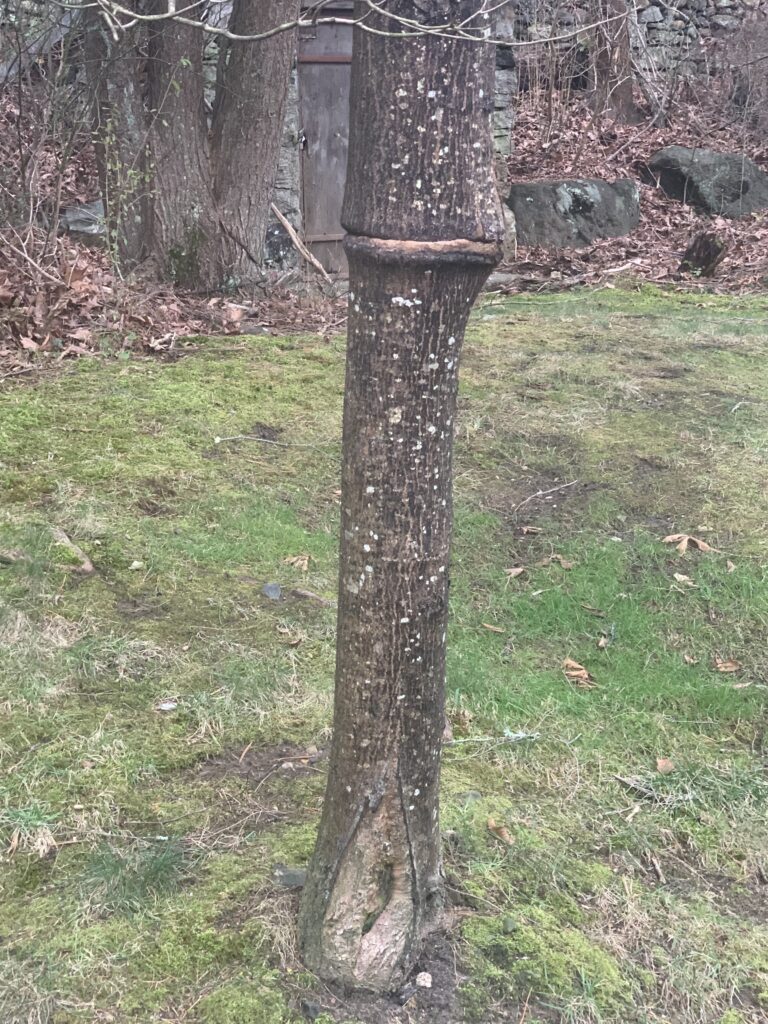


Photo: Guy Pardee

Photo: Guy Pardee
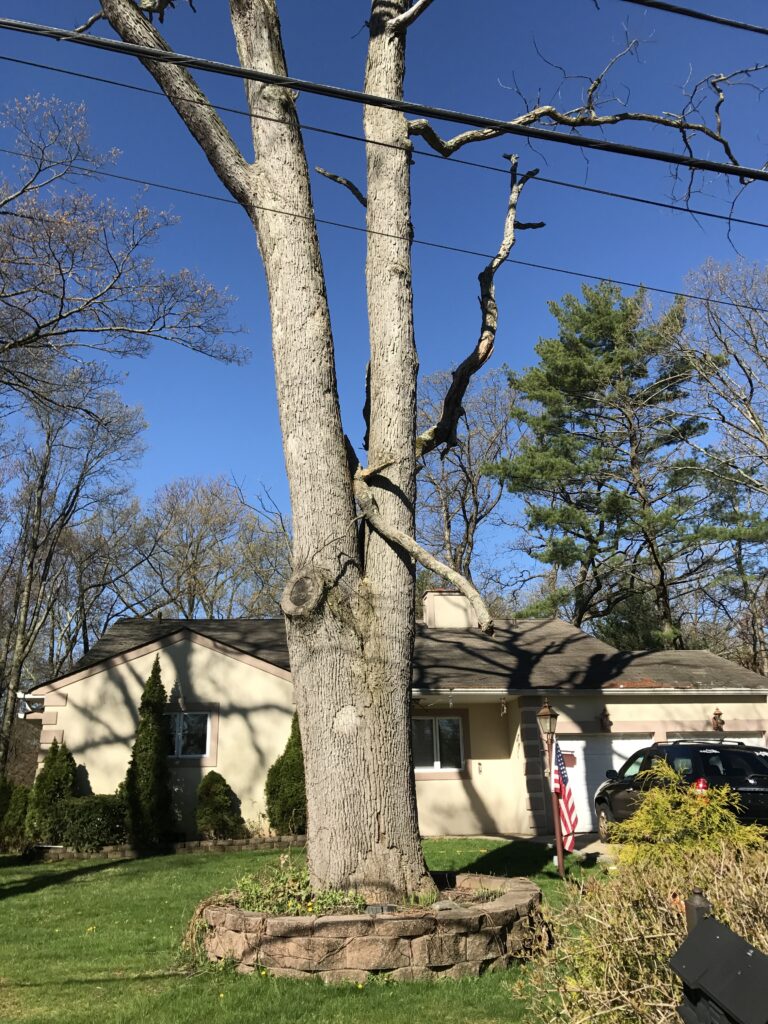
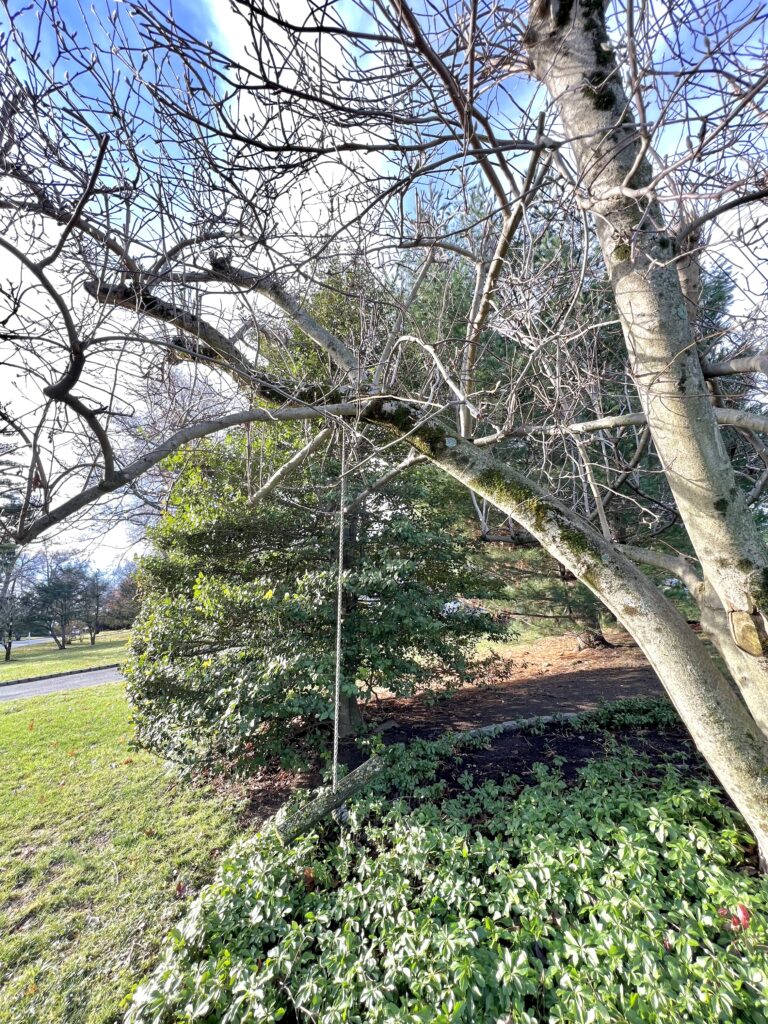
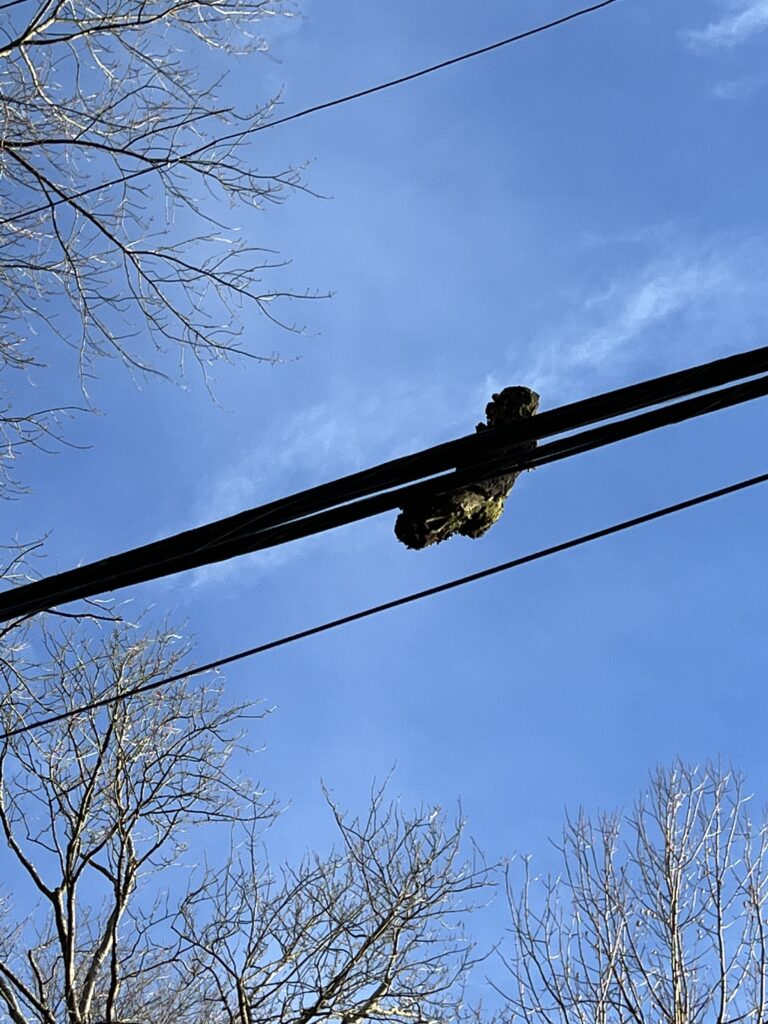
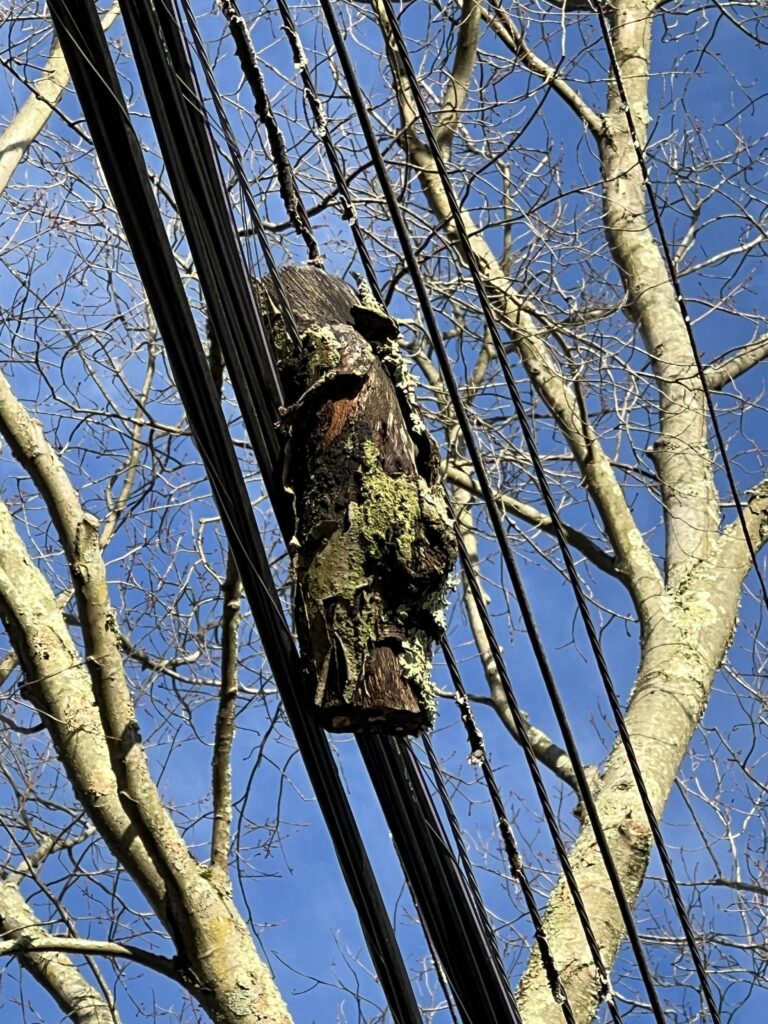
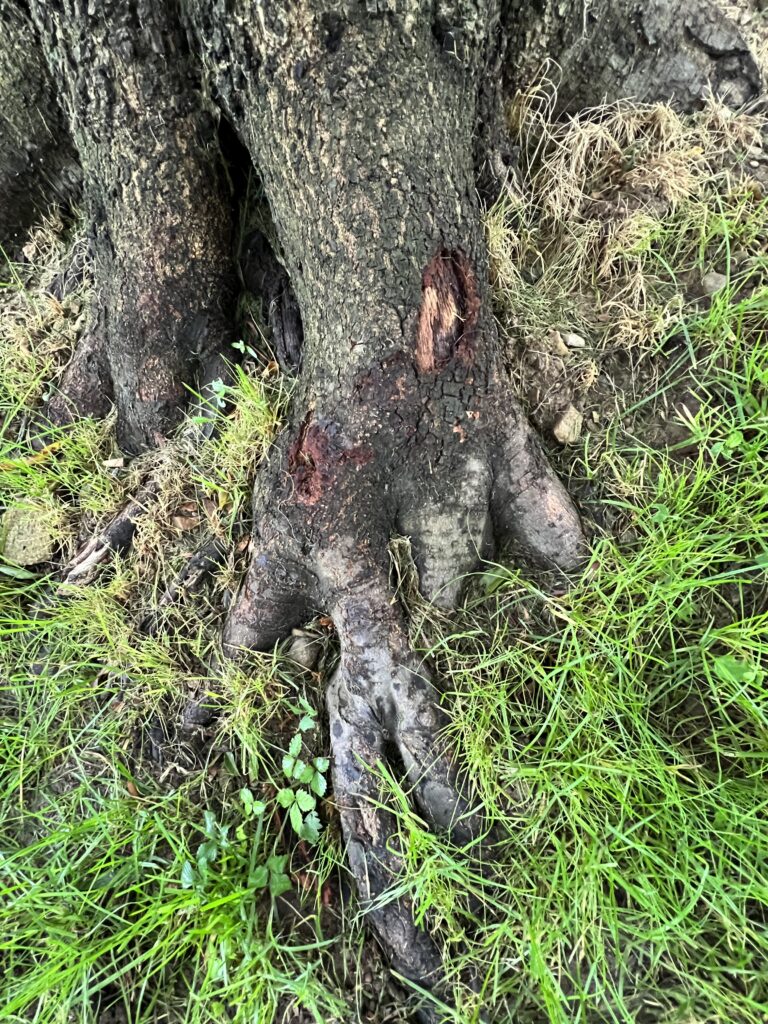
Hanging swings, hammocks, and bird feeders from tree branches can also cause damage. Allowing tree trunks or branches to rest against power lines, big rocks, and fences is another hazard.
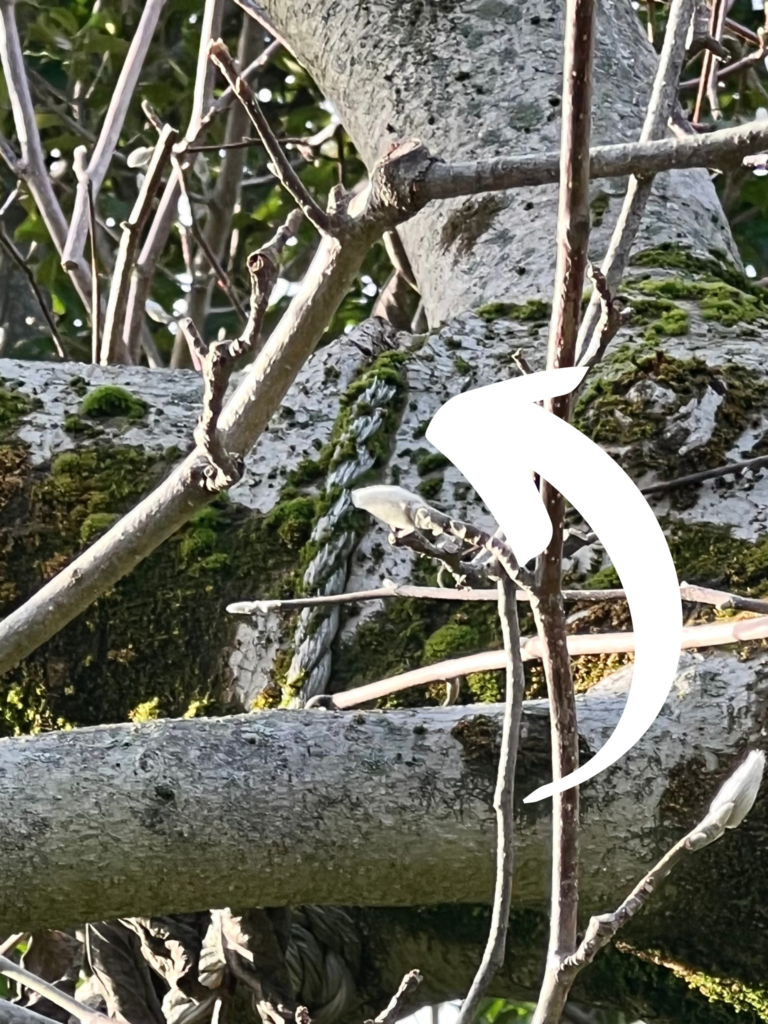





Another common error is incorrect planting that can result in a tree being girdled by its own roots. If a young tree has been in a nursery container too long, the roots may wrap around the base of the tree within the container. At planting, care should be taken to gently unwrap the roots and extend them away from the trunk in a hole wider than it is deep.
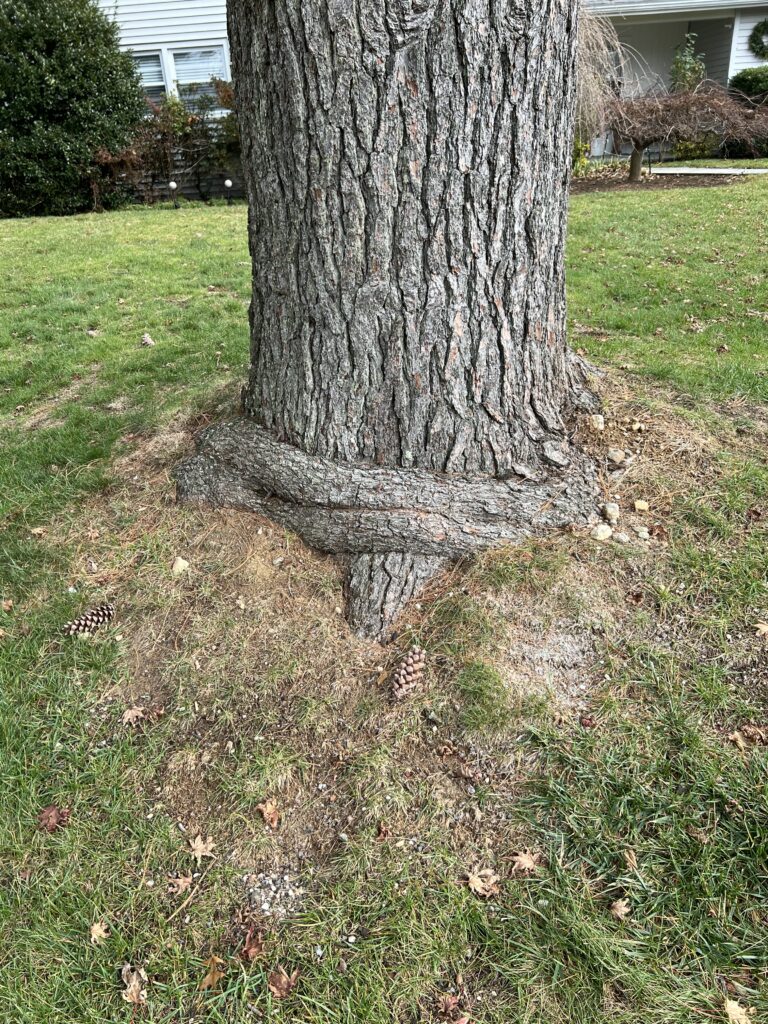

Though trees may survive partial girdling by roots, they will be more vulnerable to storm damage and disease. Consult an experienced certified arborist to evaluate possible remedial action if the tree and girdling roots are in an advanced stage.
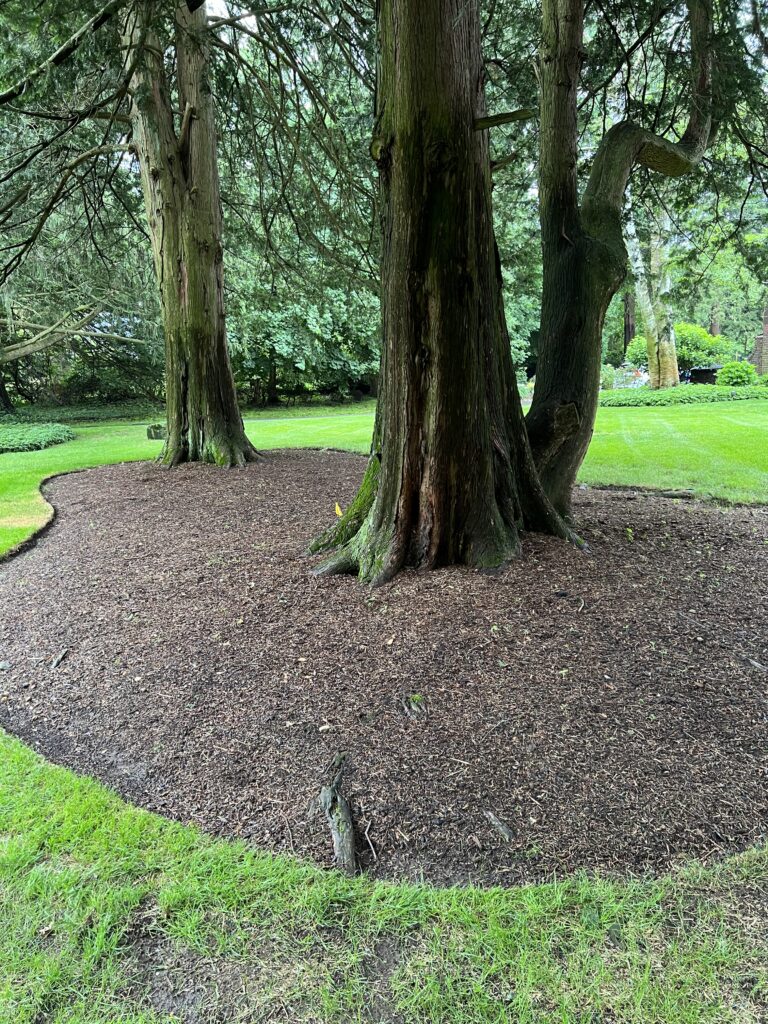
Although tree trunks merge with tree roots near the soil line, it is important to recognize that trunks and roots are not the same. Tree trunks “flare” at the base just above the root zone. If the flare is buried beneath the soil line, or by too much mulch, excess moisture can cause the protective outer bark to rot, exposing the living inner layers to mold, fungus, insects, and disease – effectively girdling the trunk at the soil line.
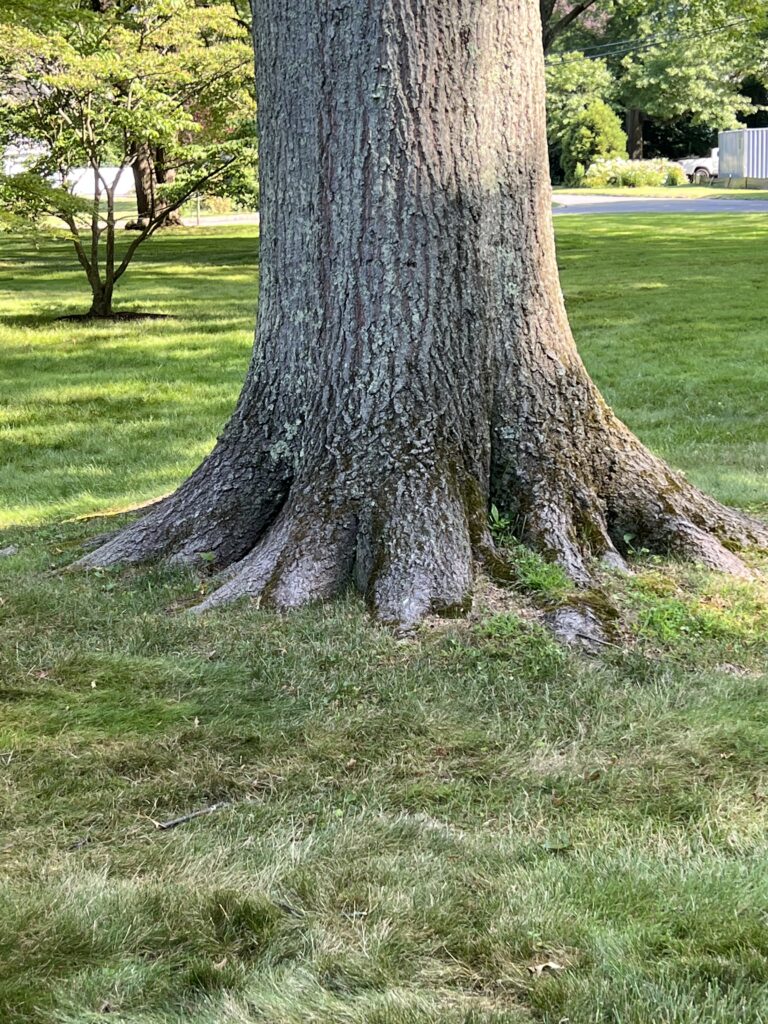
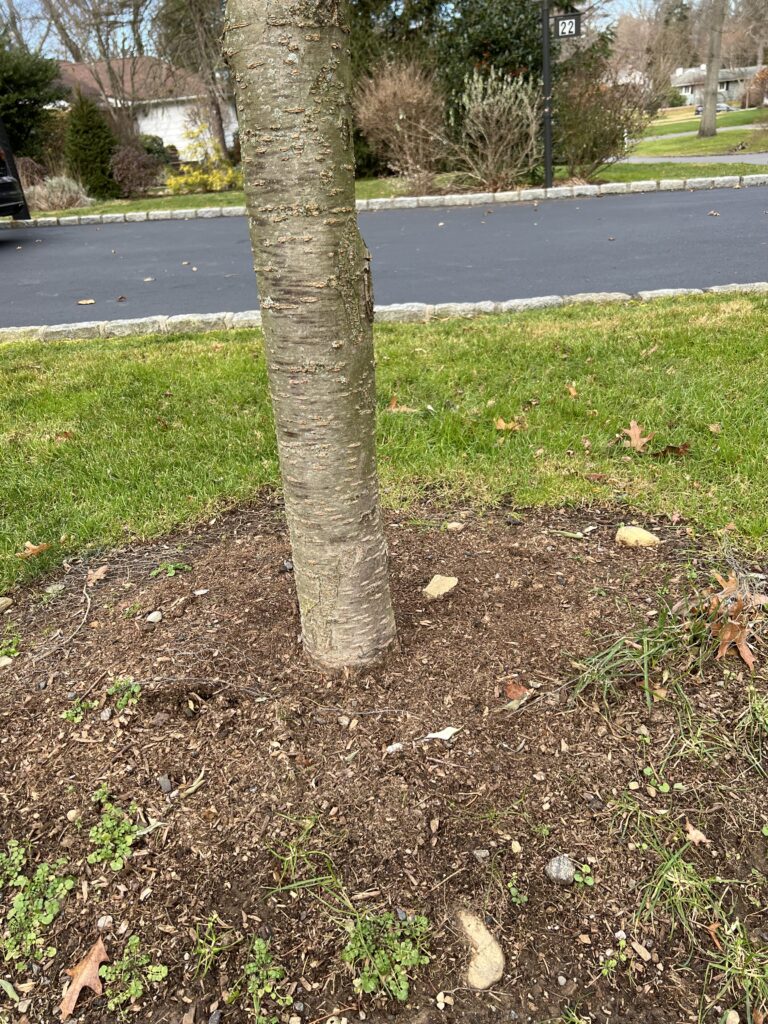


Lawnmowers, construction equipment, deer, and invasive vines all can damage trees by wounding the living outer layers of the trunk.



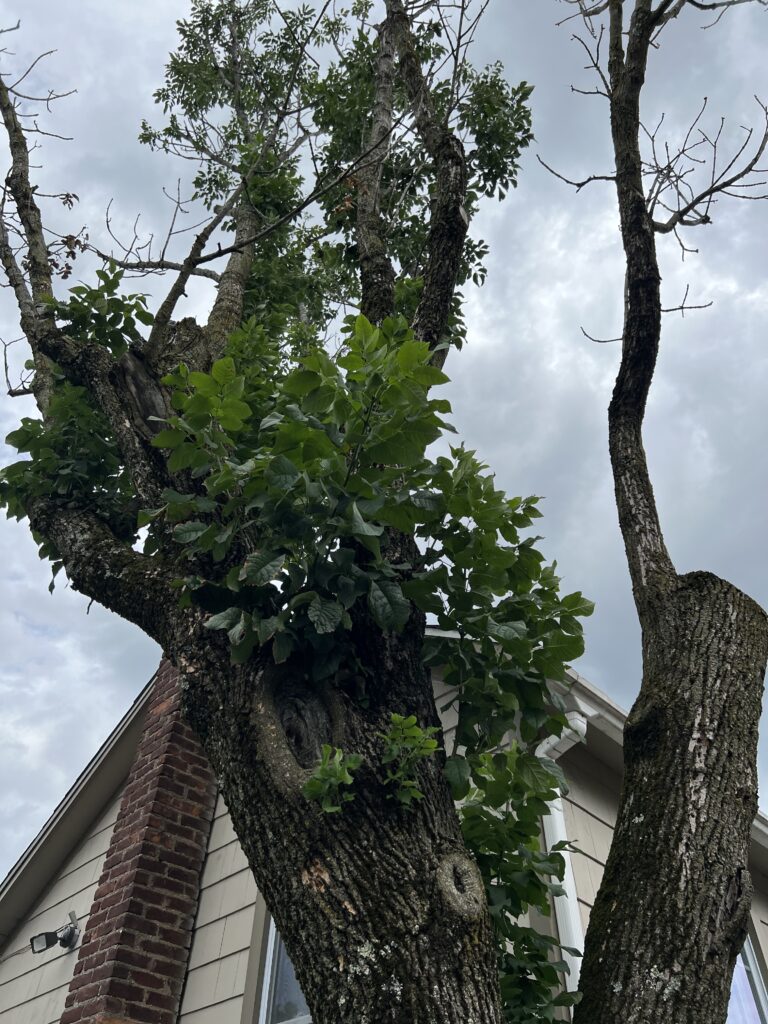
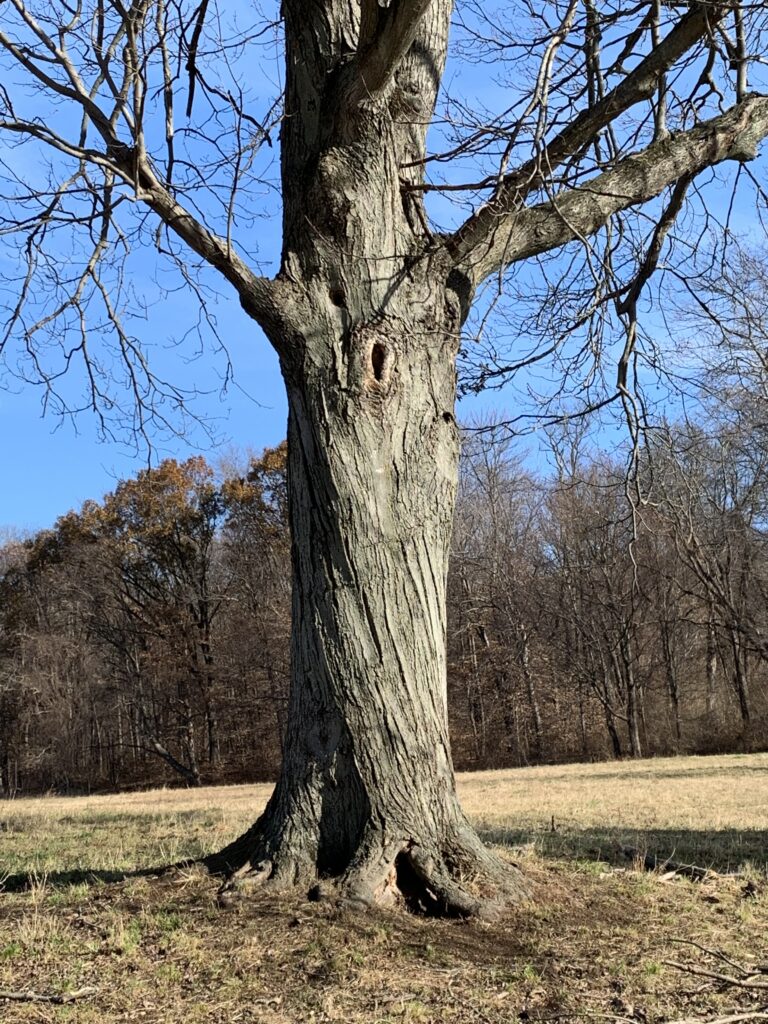
Trees are strong enough, and adaptable enough, to share their life forces with other living things. They will work around a hole that supplies shelter for an owl or squirrel family. They can survive for decades with a virtually hollow interior because their living and growing happens on the outside. But it’s up to us to protect them from careless damage so they can continue to save the world.

For more on tree care, make sure to read last week’s post,
For the Love of Trees
THIS BLOG IS AUTHORED WEEKLY BY CATHY LUDDEN, CONSERVATIONIST AND NATIVE PLANT EDUCATOR; AND BOARD MEMBER, GREENBURGH NATURE CENTER. FOLLOW CATHY ON INSTAGRAM FOR MORE PHOTOS AND GARDENING TIPS @CATHYLUDDEN.
To subscribe to the blog — and nothing else — enter your email below.













































