The morning news is just awful: wars, school shootings, forest fires, floods, political extremes. It’s all too much, and I think I can actually feel my blood pressure rising. Stressed and depressed, I turn away from the news, and look out my window…
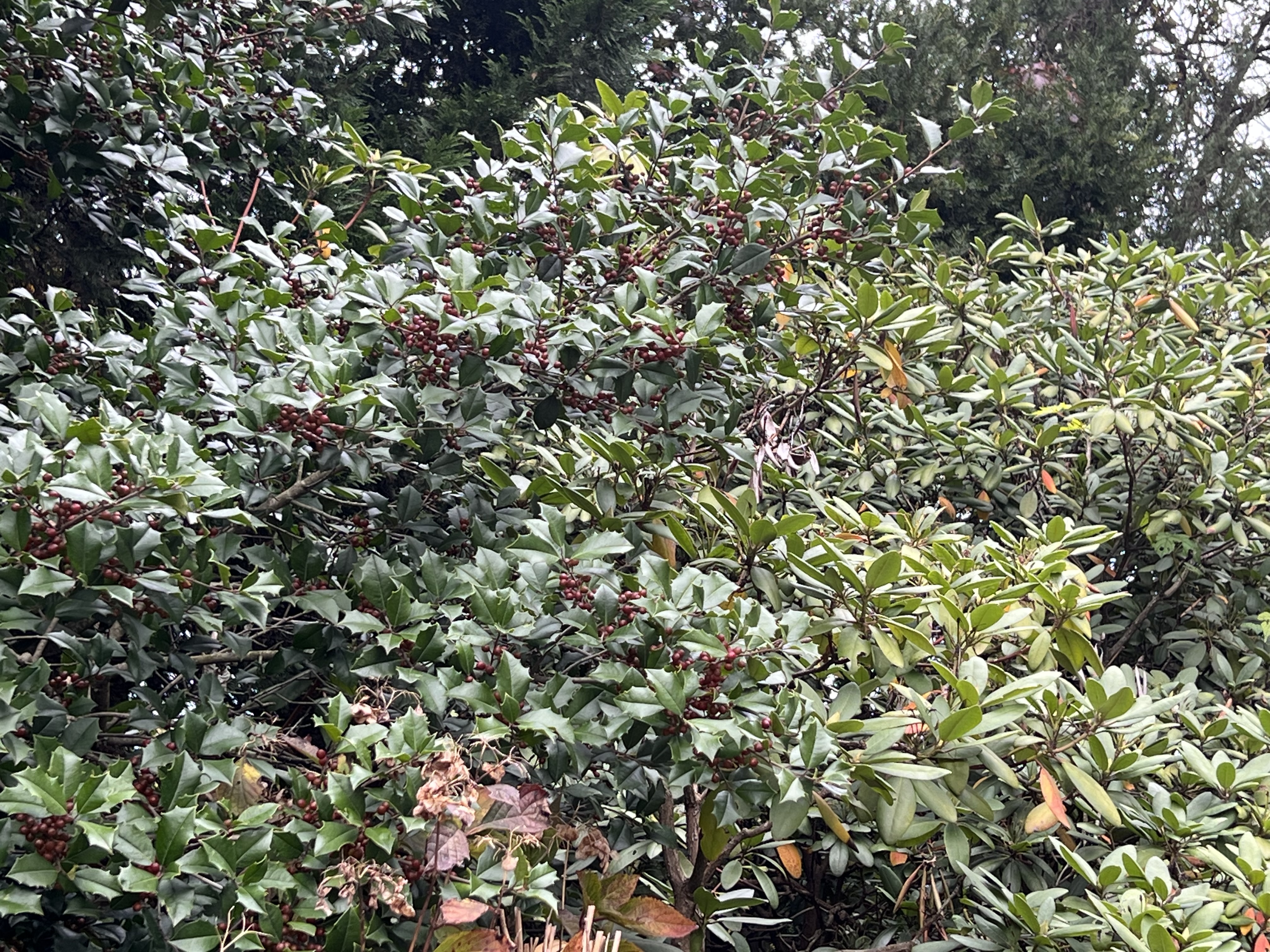
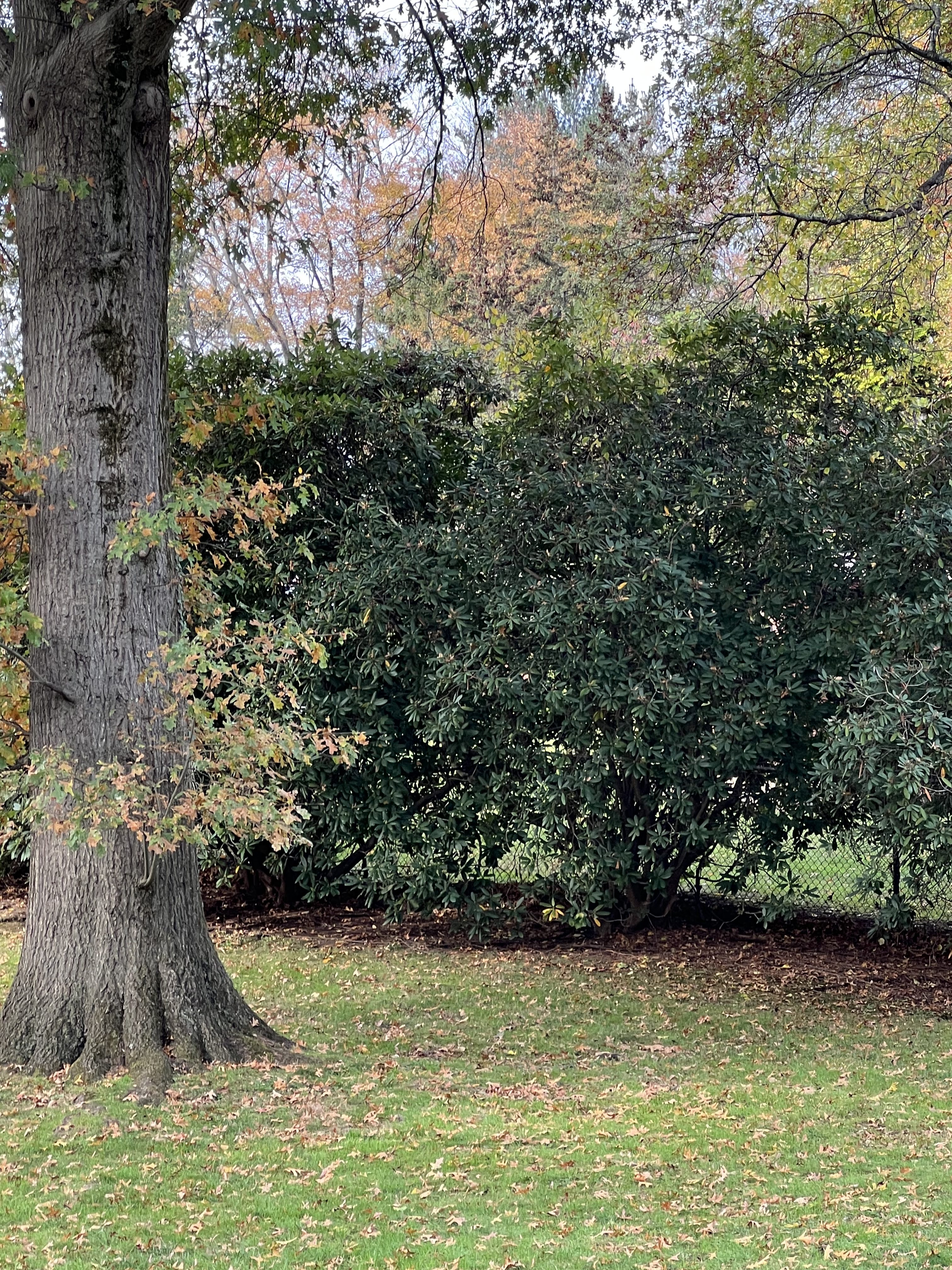
A big flock of robins has descended on the Winterberry, eating berries as fast as they can in a joyful feast! They dash back and forth between the Winterberry and the Crab Apple as if they can’t decide which fruit they like best. Dozens more birds – robins, blue jays, and cardinals dive into the American Holly. Squirrels grab the berries knocked to the ground and scamper off to stash them for later.
As I step outside to watch the action, I hear crows screeching an alert from the top of the Locust trees. Sure enough, I see a red-tailed hawk circling high above. Out of the corner of my eye, I notice a rabbit dash for cover under the mess of flower stalks I’ve left standing for just that reason – it’s a great place to hide!

Watching all of this, I realize that I’m now smiling and calm. The tension I felt earlier has receded. My pulse and breathing have slowed, and there is a sense of well-being just from spending a few minutes in my own yard. These are the healing side-effects of living in nature!
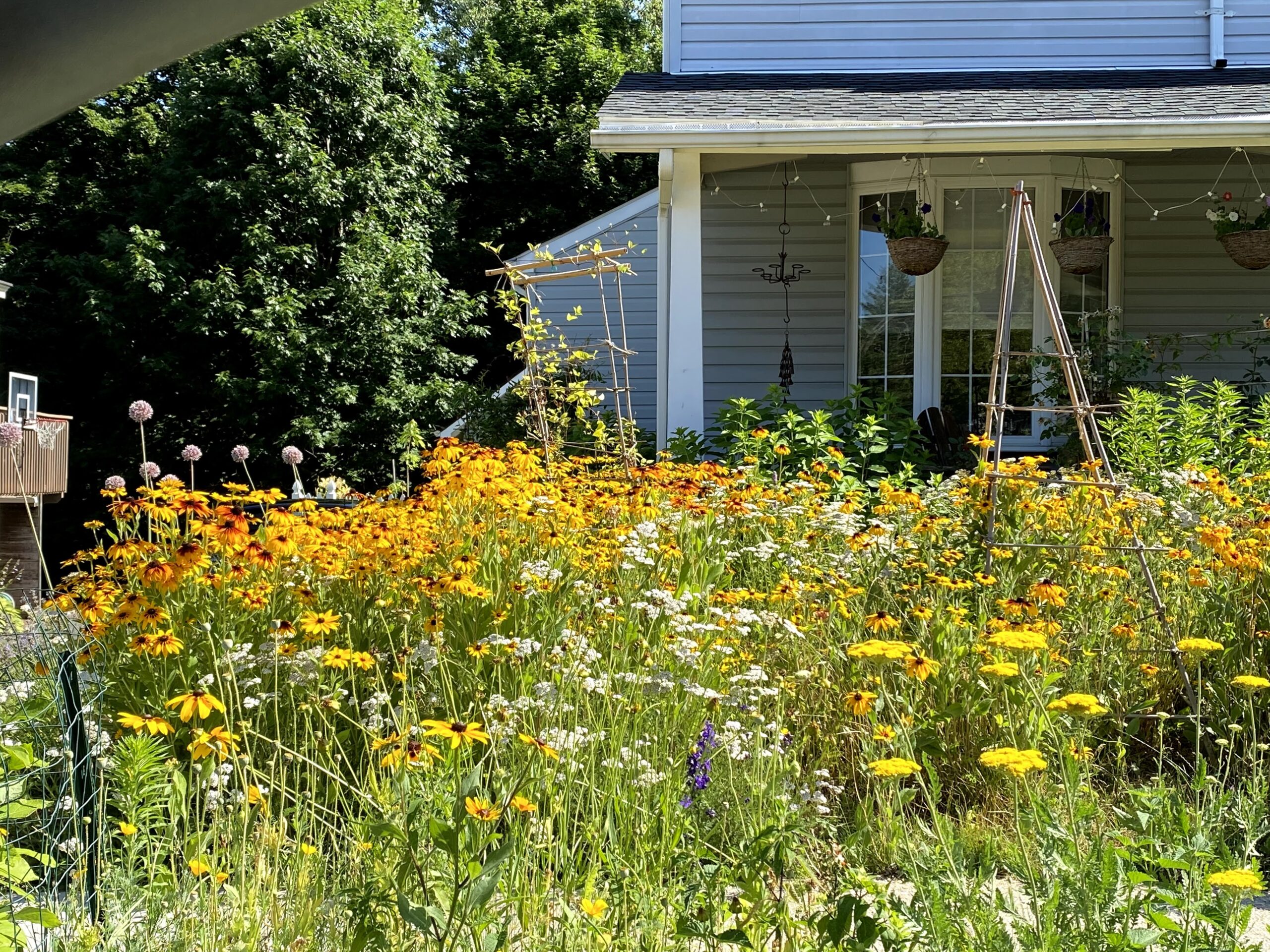
My yard is not typical of suburban New York City. It is heavily planted with native trees, shrubs, grasses, and flowers. It’s intentionally a bit messy this time of year, with leaves still on the ground, and untrimmed perennials and tall grasses in muted shades of brown and beige still standing. The shrubs are not clipped into tidy shapes but are allowed to form thickets with their branches interlaced. There is a brush pile creating shelter against the back fence, and River Birch trees with shaggy bark hide insects for woodpeckers and nuthatches even in winter.

I know that is why the birds are here: there is food and shelter available year-round in this particular suburban yard.
About 10 years ago, I eliminated pesticides, herbicides, and chemical fertilizers from my yard. Then I began removing the non-native and invasive plants so typical of our area: ivy, vinca, pachysandra, barberry, and burning bush. I gradually replaced them with lots of native trees, shrubs, grasses, and flowers, always chipping away at the lawn to make more room. I stopped sending fall leaves off of the property and started using them to mulch the trees and shrubs, so the fireflies and caterpillars over-wintering in leaves could stay alive and emerge in the spring. Eventually, I replaced more than half of my lawn with native plants.

I did all of this because I learned that American songbirds are dying off at a horrifying rate. The total population of backyard birds today is 25% less than it was in 1970, and many once common species have lost closer to 50% of their numbers! Baltimore orioles, bluebirds, and warblers were once as common as robins, but are rarely seen now. This is happening because the forests, meadows, and grasslands where birds once nested, mated, and hunted for insects are gone.
There is virtually no undeveloped land left in America. The suburbs keep growing, taking over land that only a few decades ago was wild. Today, 83% of the continental US is privately owned, and 44 million acres of it is planted in lawn! Worse, most of that lawn is maintained with chemicals that are toxic to birds, butterflies, fireflies, and insects that birds need to feed their young.

Yet, America’s suburbs may be “nature’s best hope.” It’s really the only land left that can be reclaimed as a useful habitat. In the book, Nature’s Best Hope, Doug Tallamy suggests that if we converted just half of the lawn in suburbia — 22 million acres — to native plants, it would exceed the combined areas
…of the Everglades, Yellowstone, Yosemite, Grand Teton, Canyonlands, Mount Rainier, North Cascades, Badlands, Olympic, Sequoia, Grand Canyon, Denali, and the Great Smoky Mountains National Parks.
That much habitat could have a huge impact on biodiversity – even reversing losses of vital and cherished bird and animal species. These facts were the motivation for my effort to convert a typical lawn-and-tidy-shrub suburban landscape into something richer and more diverse.
I thought I was doing it for nature. The surprise has been what nature does for me!
My yard full of native plants is my refuge, my laboratory, my classroom, my gym, my anti depressant, my stress reliever, and a playground for our family’s children that is infinitely more
interesting and safer than a lawn full of chemicals. We’ve seen new species of butterflies settle here after I added their host plants. With more birds around, we started learning to identify
them. So far, we have identified over 40 different species! And I’ve seen wonderful things I had never before even heard of, like a hummingbird moth!
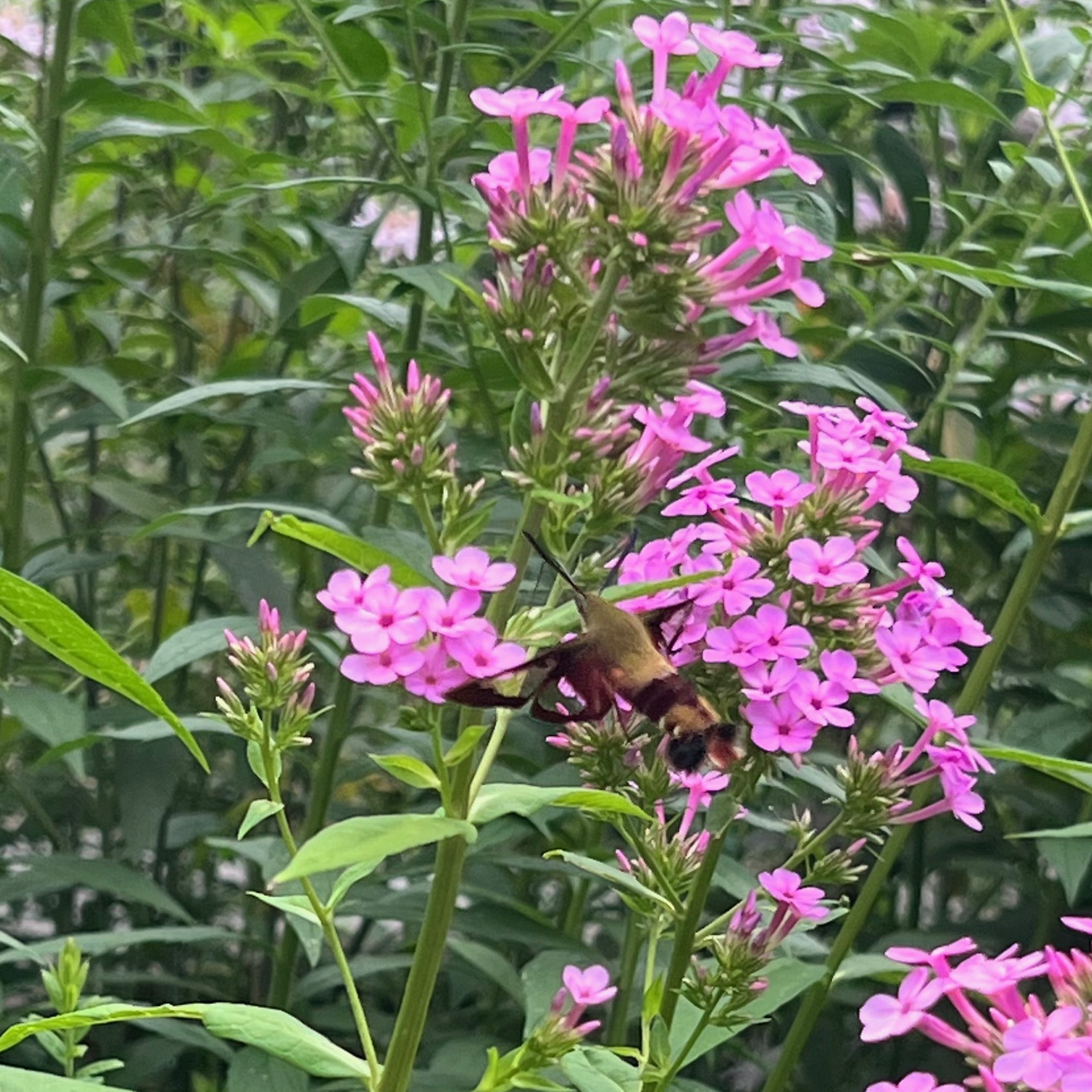

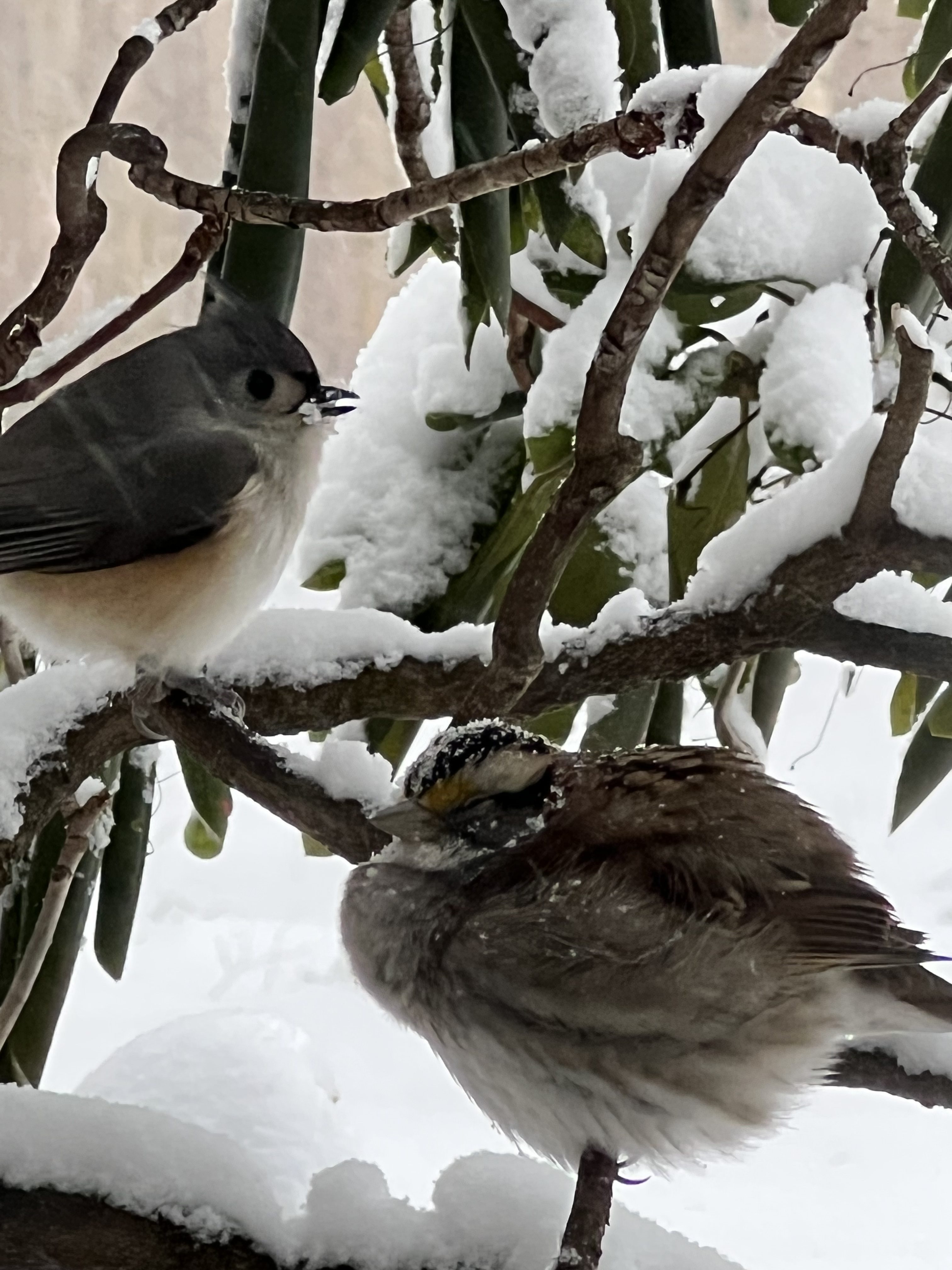
There is something new to discover almost daily in a bio-diverse landscape. It is full of life and wonder! The seasons change so visibly: delicate spring flowers, fragrant summer shrubs, so many fall colors, and winter bird feasts! The sounds are amazing: bird calls, crickets, tree frogs, cicadas, and squirrels chittering. The experiences make me feel alive: watching fireflies blink on a summer evening while the air is filled with the perfume of Summersweet shrub; watching from my living room window as tiny birds take refuge from a snowstorm.

When the stress of daily life is just too much, you can always visit the Nature Center, or take a walk in any park or nature preserve. It will help.
But it’s so much better to live with nature, and in nature, in your own yard! You can welcome it, take care of it, observe it, learn from it, and be surprised by it every time you step outside. As we begin the new year, I hope you will resolve to convert a bit more of your yard to habitat and do it not only for nature but for yourself and your family.
There are simple things you can do that will make a difference. This blog frequently has suggestions, so scroll through the Around the Grounds Collection below, or start with these posts for ideas: (1/26/23, 2/16/23, 3/23/23, 4/27/23, 10/5/23).
Wishing you joy, peace, and delight in the new year!
Thanks to Saverio DeGiorgio for the featured photo. Follow Sav on Instagram @savwildlifephotography
THIS BLOG IS AUTHORED WEEKLY BY CATHY LUDDEN, CONSERVATIONIST AND NATIVE PLANT EDUCATOR; AND BOARD MEMBER, OF GREENBURGH NATURE CENTER. FOLLOW CATHY ON INSTAGRAM FOR MORE PHOTOS AND GARDENING TIPS @CATHYLUDDEN.